Did you know that an astounding 7 out of 10 cases of cardiac arrests can be successfully resuscitated through the implementation of CPR? The potential to save lives is immense. Tragically, numerous notable individuals have succumbed to cardiac arrests, including the distinguished APJ Abdul Kalam, former President of India. He encountered this unfortunate event while delivering a lecture at a prestigious educational institution in Shillong. Amidst his lecture, Dr. Kalam suffered a sudden cardiac arrest, collapsing without warning. It leaves us to ponder whether prompt administration of CPR could have altered the outcome, although we can only speculate. Dr. Kalam serves as a mere illustration, as anyone could find themselves in a similar situation, underscoring the significance of CPR as a life-saving measure.
What in the world is CPR?
In simple terms, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a life-saving procedure used during emergencies when someone’s heart has stopped or is not pumping blood properly. The main goal of CPR is to bring back blood flow and provide oxygen to the brain. It acts as a vital link between the time a cardiac arrest happens and when professional medical help arrives. Knowing what CPR involves and how it can help in critical situations is essential for everyone to make a difference and potentially save lives.
Who should learn CPR?
Now, this is an easy question! EVERY SINGLE PERSON!!! You never know when this simple skill may prove to be essential.
Learn CPR today and become the hero who saves lives tomorrow.
– Dr. Abraham Mallela
How to perform CPR?
Performing CPR involves the following steps:
- Check for scene safety: The first important aspect of initiating CPR is to first assess the safety of the surrounding scene. This step, known as checking for scene safety, ensures the well-being and security of both the rescuer and the person in need.
- Check the person’s responsiveness: Gently stimulate or tap their shoulder and loudly inquire, “Are you okay?” If there is no response, it indicates the need for CPR. If you have a bit of medical knowledge, try to locate a pulse on the victim, preferably near the neck, but it is crucial not to waste too much precious time doing so.
- Call for assistance: Dial the emergency number (e.g., 911 (USA) / 108 (India) / 999 & 112 (UK and Europe)) or request someone nearby to summon professional medical help. Promptly contacting emergency services is crucial during a cardiac event.
- Position the person: Place the individual in a supine position on a stable and hard surface.
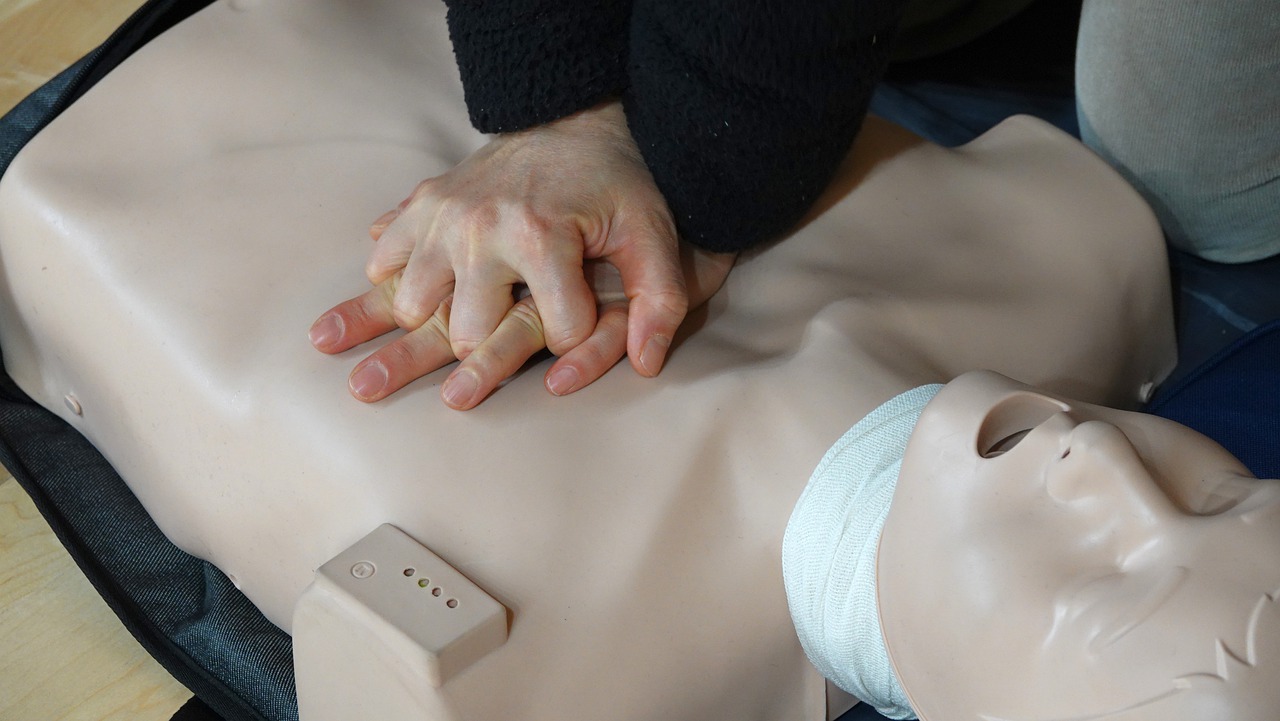
- Initiate chest compressions: Position the heel of one hand precisely at the center of the person’s chest, typically between the nipples. Overlap the other hand and interlock your fingers. Maintain straight arms and align your shoulders directly above your hands.
- Administer forceful and rhythmic compressions: Apply adequate pressure, utilizing your body weight, to depress the chest. Aim for a compression depth of at least 2 inches while maintaining a rate of approximately 100 compressions per minute. Allow the chest to fully recoil after each compression.
- Provide rescue breaths: If you possess CPR training and feel competent, you may perform rescue breaths. Slightly tilt the person’s head backward, lift their chin, and pinch their nose. Inhale a normal breath, create a seal with your mouth over theirs, and deliver breaths until their chest visibly rises. Administer a second rescue breath.
- Continue cycles of compressions and breaths: Repeat the sequence of 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths. Sustain this pattern until professional assistance arrives or the individual exhibits signs of recovery, which is known as Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC).
- Employ an automated external defibrillator (AED) if available: If an AED is accessible, use the device as instructed. Follow the voice prompts, attach the electrode pads to the person’s exposed chest, and maintain a clear area during the AED’s analysis of the cardiac rhythm. If advised, administer a shock, ensuring no physical contact with the person when delivering the electrical therapy.
- AEDs are now a common device that can be easily found, with the latest government regulations making them mandatory in public places as well as big establishments.
The following video shows the actual process of CPR : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yBfpSnAHX9Q&t=248s
Remember, even if you lack formal CPR training, performing chest compressions alone can still significantly contribute to the person’s chances of survival. The primary objective is to maintain blood circulation until medical professionals assume control of the situation.
CPR is not just a set of skills or a medical procedure; it is a powerful tool that transforms ordinary individuals into everyday heroes. By learning CPR and being prepared to take action during critical moments, you have the potential to save lives and make a profound difference in your community.
Every passing moment offers an opportunity to become that hero waiting to be found. Imagine the impact you could have when faced with an emergency, when a person’s life hangs in the balance. By swiftly initiating CPR, you become a beacon of hope, bridging the gap between life and death, and instilling a second chance at life.
You can learn CPR by asking someone who is trained in Basic Life Support (BLS) to teach you or by attending community outreach programs conducted by hospitals and other medical establishments.
This is a picture of me training the officers of Raheja Mindspace IT Campus in Hyderabad.